I. PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES

1. Principle of Operation
An Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) is a type of engine in which fuel is burned directly inside the combustion chamber. The heat generated from combustion produces high pressure that pushes the piston in a reciprocating motion. This linear motion is transmitted through the connecting rod to the crankshaft, converting it into rotary motion to drive machines or vehicles.
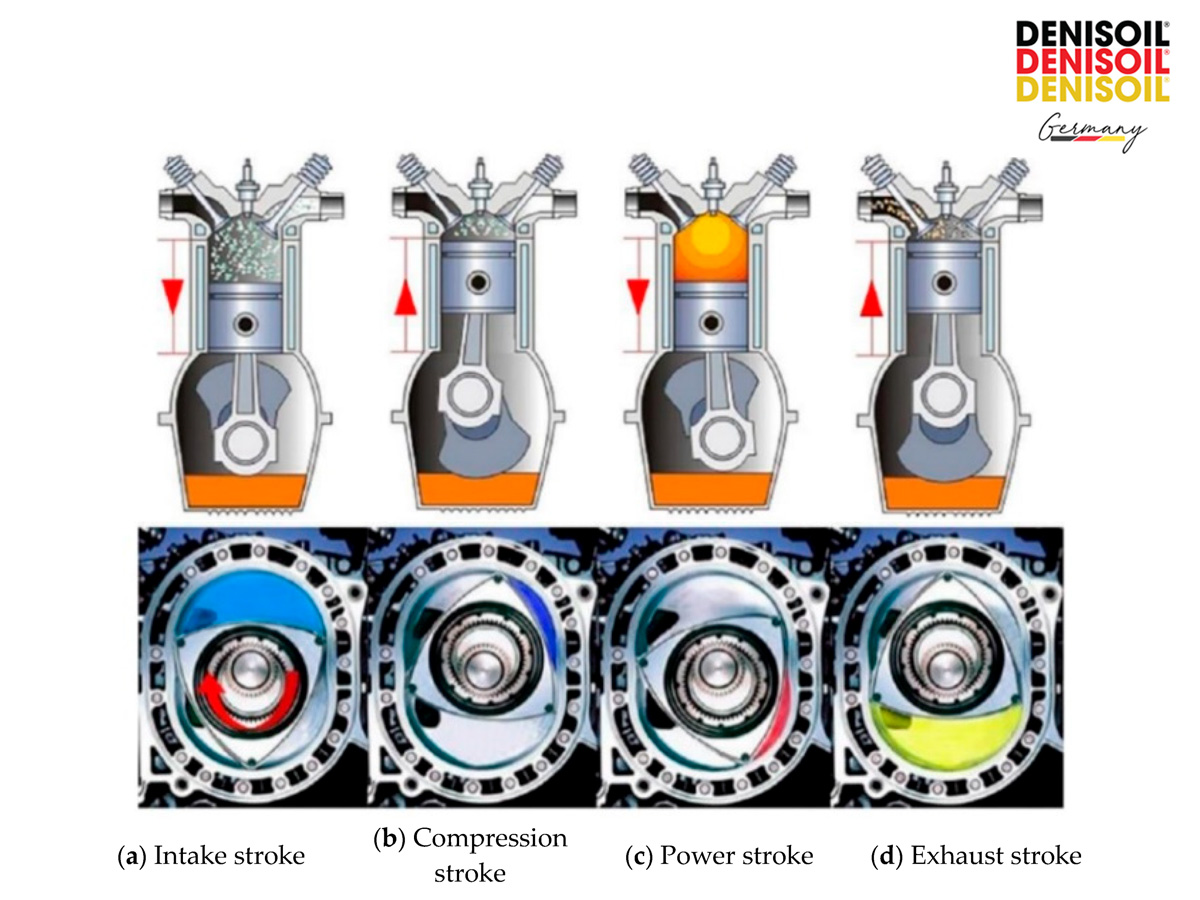
The Four-Stroke Cycle:

- Intake stroke: The piston moves downward, and the intake valve opens to draw in the air-fuel mixture (gasoline engine) or air (diesel engine).
- Compression stroke: The piston moves upward with both valves closed, compressing the mixture.
- Power stroke:
- In gasoline engines, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture.
- In diesel engines, fuel is injected into the compressed hot air and self-ignites.
The combustion produces high pressure, pushing the piston down.
- Exhaust stroke: The piston moves up again, and the exhaust valve opens to expel burnt gases.
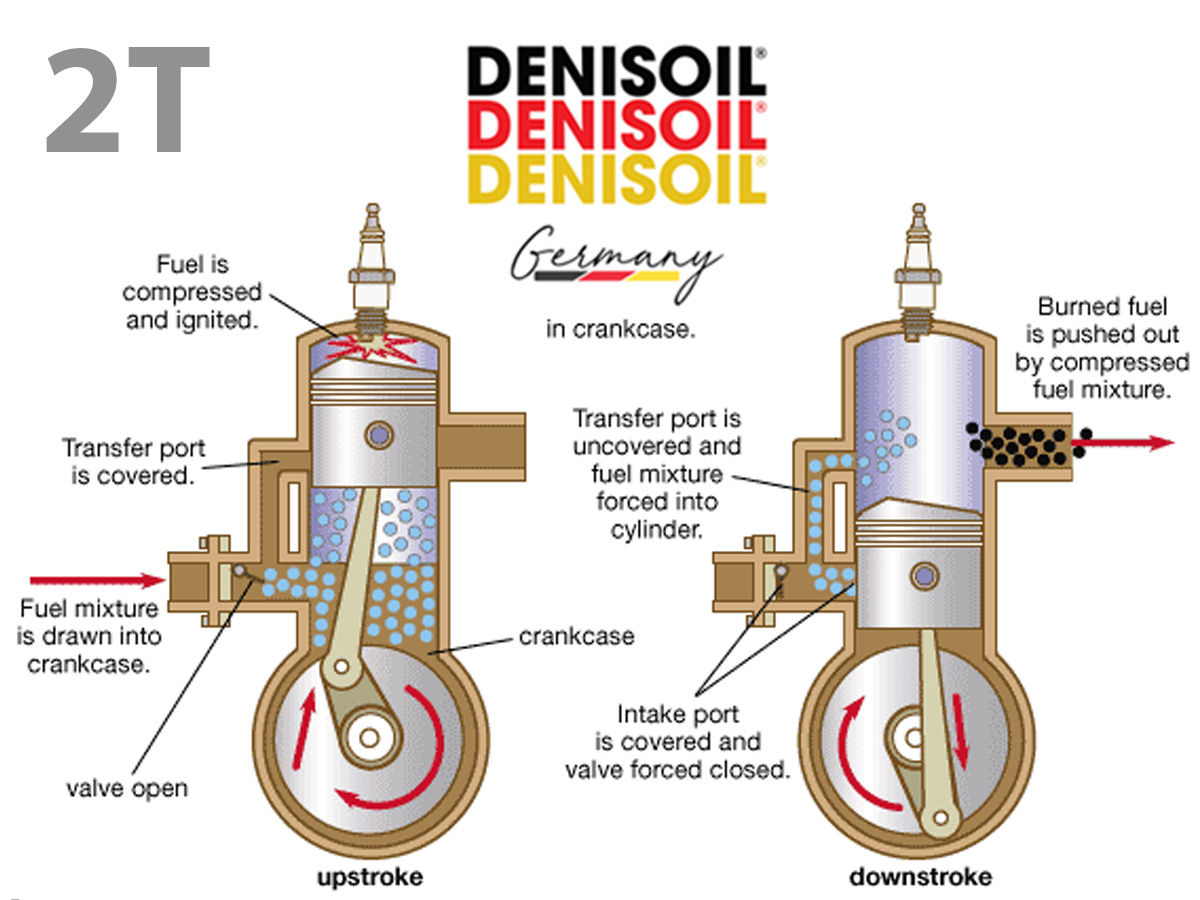
Two-stroke engines combine intake–compression and power–exhaust strokes into one cycle per crankshaft revolution, making them more compact and powerful for their size but less fuel-efficient and more polluting.
2. Classification of Internal Combustion Engines
a) By fuel type:
- Gasoline Engine (Spark Ignition – SI)
- Diesel Engine (Compression Ignition – CI)
- Gas-Fueled Engine: CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
b) By operating cycle:
- Four-stroke engine
- Two-stroke engine
c) By application:
- Automotive engines (cars, motorcycles)
- Industrial engines (generators, construction machinery)
- Marine engines (ships, boats)
II. ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES

1. Reduction of Harmful Emissions:
- CO (Carbon Monoxide)
- NOx (Nitrogen Oxides)
- HC (Unburned Hydrocarbons)
- PM (Particulate Matter)
2. Compliance with Emission Standards:
- Euro 4–6 (Europe)
- EPA Tier levels (United States)
- TCVN (Vietnamese national standards)
3. Clean Technology Integration:
- EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation): Reduces NOx by recirculating part of the exhaust gas.
- Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC): Converts CO, HC, and NOx into CO₂, H₂O, and N₂.
- DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter): Captures fine particulates from diesel exhaust.
- SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction): Uses urea (AdBlue) to convert NOx into nitrogen and water.
4. Use of Environmentally Friendly Lubricants:

- Low SAPS (Sulfated Ash, Phosphorus, Sulfur): Protects after-treatment devices (DPF, TWC).
- Compliant with standards such as API CK-4, FA-4 (USA), ACEA C1–C5 (Europe).
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Chinese
Chinese
 English
English














