I. What is Base Oil?
Base oil is the foundational component in lubricants, accounting for 70–99% of the formulation. It serves as the primary raw material in engine oils, hydraulic oils, compressor oils, gear oils, greases, and other industrial fluids.
However, base oil alone lacks ideal lubricating properties and only becomes effective when blended with additives to form finished lubricants that meet stringent technical requirements.

II. API 1509 Base Oil Classification
The American Petroleum Institute (API) classifies base oils into five groups based on:
• Sulfur content (S)
• Percentage of unsaturated hydrocarbons
• Viscosity Index (VI)
|
Group
|
Type
|
Sulfur Content
|
% Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
|
VI (Viscosity Index)
|
Origin
|
|
I
|
Solvent-refined mineral oil
|
> 0.03%
|
> 10%
|
80–120
|
Petroleum
|
|
II
|
Hydrocracked mineral oil
|
≤ 0.03%
|
≤ 10%
|
80–120
|
Petroleum
|
|
III
|
Severely hydrotreated oil
|
≤ 0.03%
|
≤ 10%
|
> 120
|
Petroleum (near-synthetic)
|
|
IV
|
Polyalphaolefin (PAO)
|
Very low
|
None
|
> 125
|
Synthetic
|
|
V
|
Esters, PAG, Silicone, etc.
|
Varies
|
Varies
|
Varies
|
Synthetic / Natural
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
III. Common Types of Base Oil

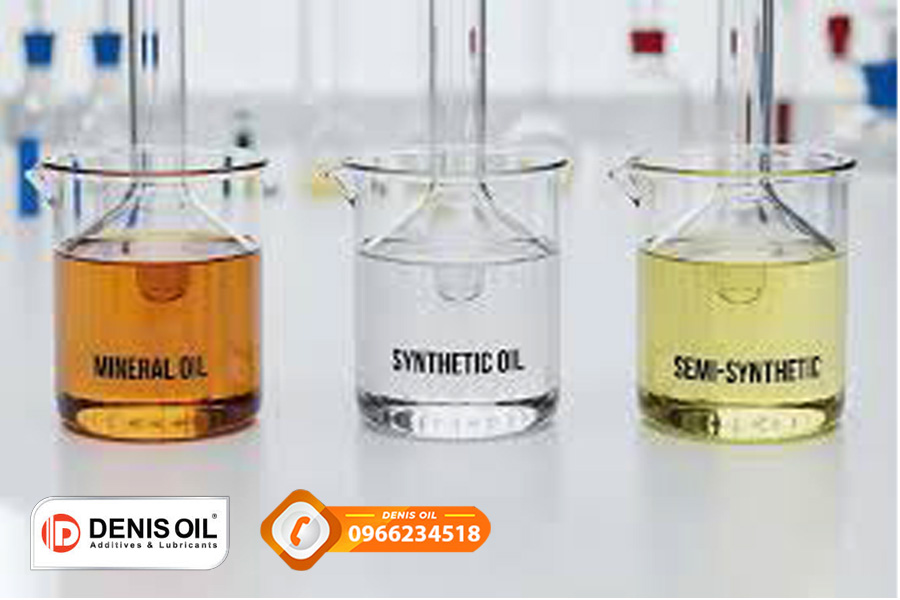
3.1. Mineral Base Oil (Groups I, II, III)
• Derived from crude oil using solvent refining, dewaxing, hydrocracking.
• Advantages: Low cost, easy to produce, suitable for standard applications.
• Disadvantages: Lower thermal and oxidative stability, more deposits.
Popular types: SN150, N150.

3.2. Synthetic Base Oil (Groups IV, V)
• PAO (Group IV): Produced from olefin polymerization → highly stable, high VI.
• Ester/PAG (Group V): Highly polar, excellent performance in harsh environments.
Advantages:
• Excellent oxidative & thermal stability
• Good low-temperature fluidity
• Low volatility, minimal deposits
Applications: Premium engines, compressors, aviation, food-grade uses.
3.3. Semi-Synthetic Oil
• Blend of Group II/III mineral oil with some synthetic base oil (PAO/Ester).
• Advantages: Better performance than mineral oil, more affordable than full synthetics.
• Applications: Motorcycle engine oils, light to medium-duty industrial use.
IV. Composition & Chemical Structure
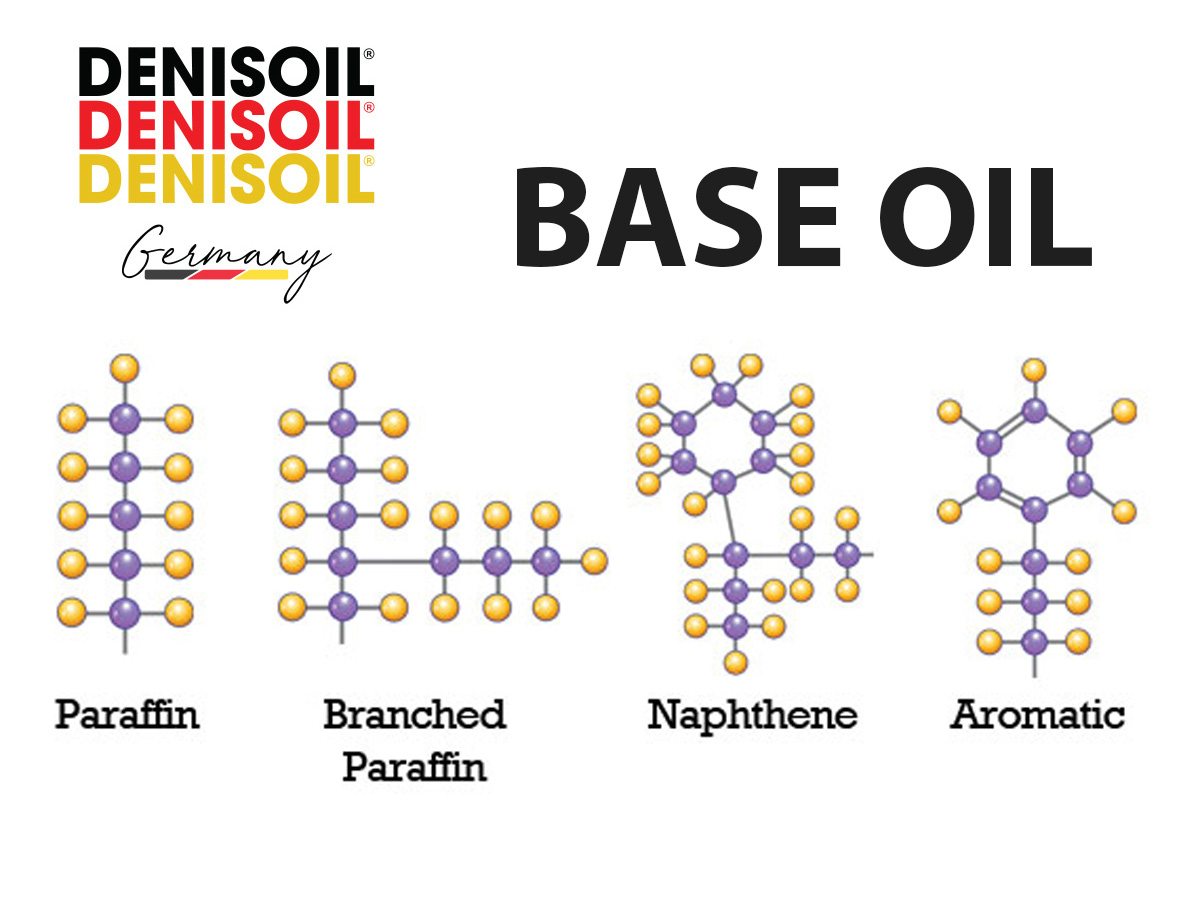
4.1. Mineral Base Oils (Groups I–III)

• Paraffinic: RCH₂–CH₂–CH₃ → stable, high VI
• Naphthenic: Cyclohexane → lower VI
• Aromatic: Benzene ring, unstable, often removed
4.2. Synthetic Base Oils (Groups IV–V)
• PAO: (–CH₂–CH(CH₃)–)ₙ → highly stable, low deposit formation
• Ester: Contains COO– group, polar, self-cleaning, heat-resistant
• PAG: Highly polar, poor compatibility, used separately
V. Key Technical Properties of Base Oil
|
Property
|
Function
|
|
Viscosity
|
Lubrication and surface protection
|
|
Viscosity Index (VI)
|
Maintains viscosity with temperature change
|
|
Low Volatility
|
Reduces oil loss at high temperatures
|
|
Oxidation Stability
|
Prevents degradation over time
|
|
Heat & Deposit Control
|
Protects system, extends equipment life
|
|
Additive Compatibility
|
Ensures stable blending and performance
|
VI. Base Oil Production Flowchart
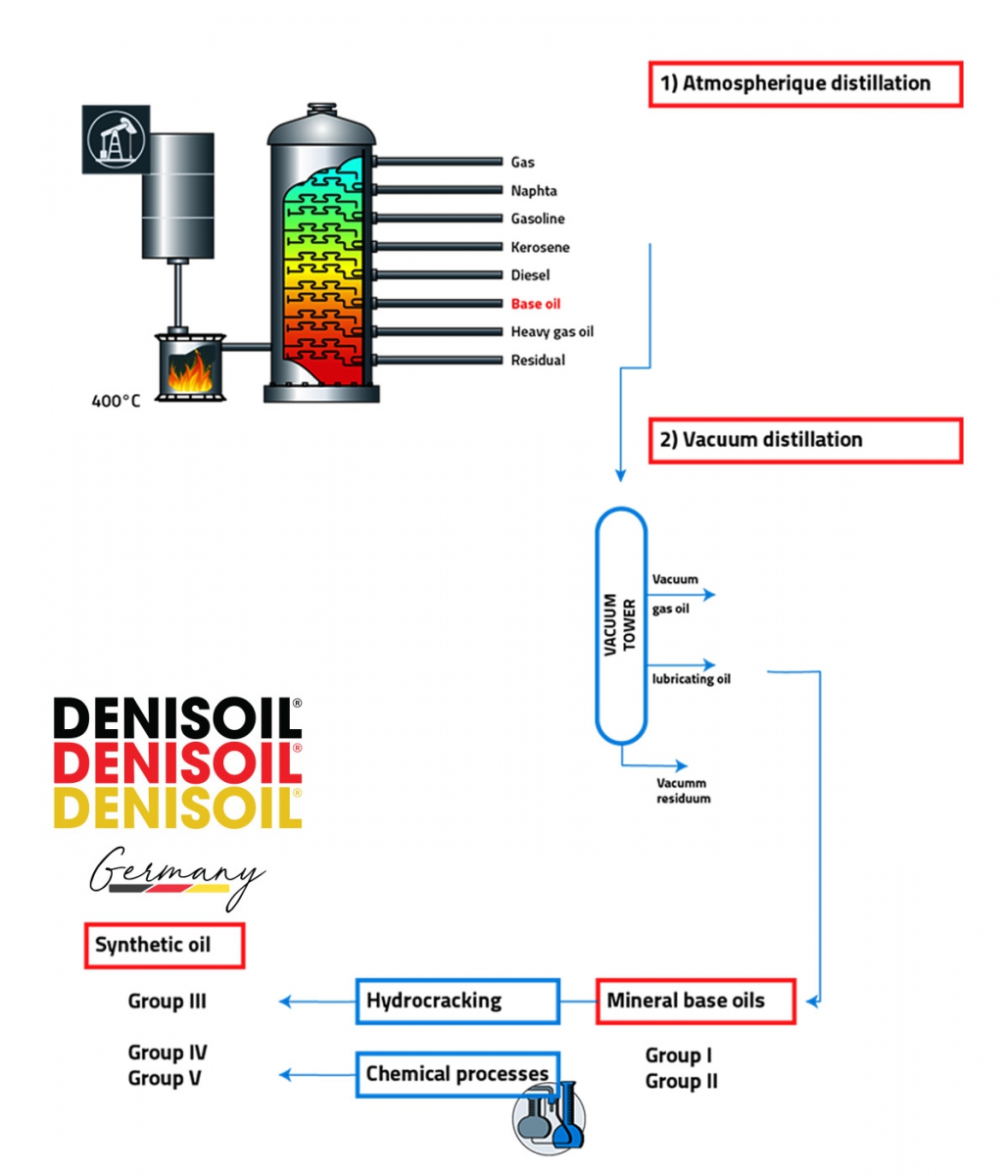
6.1. Mineral Base Oil:
A [Crude Oil] → B [Light Fraction Separation]
→ C [Solvent Refining / Hydrocracking]
→ D [Desulfurization & Dewaxing]
→ E [Hydrofinishing / Isomerization]
→ F [Base Oil Group I/II/III]
6.2. Synthetic Base Oil:
G [Pure Hydrocarbons] → H [Polymerization / Esterification]
→ I [PAO / Synthetic Ester Base Oil]
VII. Applications by Base Oil Group
|
Group
|
Typical Applications
|
|
I
|
Industrial lubricants, older engines
|
|
II
|
General engine oils, hydraulic fluids
|
|
III
|
Truck oils, high-performance engines
|
|
IV
|
Aviation, extreme environments
|
|
V
|
Refrigeration, food industry, specialty fluids
|
VIII. Technical Comparison Table
|
Property
|
G.I
|
G.II
|
G.III
|
G.IV (PAO)
|
G.V (Ester/PAG)
|
|
Cost
|
Low
|
Mid
|
Mid–High
|
High
|
Very High
|
|
Oxidation Stability
|
Avg
|
Good
|
Very Good
|
Excellent
|
Varies
|
|
Low Temp
|
Poor
|
Avg
|
Good
|
Very Good
|
Very Good
|
|
High Temp
|
Avg
|
Good
|
Very Good
|
Very Good
|
Very Good
|
|
Compatibility
|
Good
|
Good
|
Good
|
Good
|
Limited
|
|
VI (Index)
|
80–120
|
90–120
|
>120
|
>125
|
100–180
|
IX. Typical Viscosity Values


|
Base Oil Type
|
Viscosity @40°C (cSt)
|
Viscosity @100°C (cSt)
|
VI
|
|
Group I SN150
|
32–36
|
~5.4
|
~95
|
|
Group II N150
|
32–34
|
~5.5
|
~110
|
|
Group III 4cSt
|
~40
|
~7.0
|
125–135
|
|
Group IV PAO 4
|
~40
|
~7.1
|
>140
|
X. Practical Use & Recommendations
|
Application
|
Recommended Base Oil
|
Reason
|
|
High-performance engines
|
Group III / IV / V
|
Thermal stability, anti-wear
|
|
Air compressors
|
Group II / IV
|
Low volatility, stable
|
|
Cold hydraulic systems
|
Group III / IV / V
|
Good fluidity
|
|
Food/Pharma processing
|
Group V (Safe Esters)
|
Meets NSF / FDA standards
|
XI. Base Oil Compatibility
|
Combination
|
Compatibility
|
Notes
|
|
Group I ↔ II
|
OK
|
Common blend
|
|
Group II ↔ III
|
OK
|
Easy to mix
|
|
Group III ↔ PAO
|
OK
|
Used in semi-synthetics
|
|
PAO ↔ Ester
|
OK, conditional
|
Ester enhances polarity
|
|
Ester ↔ PAG
|
NOT OK
|
Incompatible
|
|
PAG ↔ Groups I–IV
|
NOT OK
|
Phase separation, use separately
|
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
 Chinese
Chinese
 English
English














